 The learning strategy Six Thinking Hats was developed by Edward de Bono, and is about how you think.
The learning strategy Six Thinking Hats was developed by Edward de Bono, and is about how you think.
De Bono categorizes thoughts as follows:
- White: Information, facts – as many and as much as possible, without interpretation and meaning: Keep it objective
- Red: Intuition, emotion: Subjective
- Black: Caution and what-ifs: Find weaknesses
- Yellow: Hope, creativity, see the positive: Find opportunities
- Green: Ideas, Solutions: Find solutions
- Blue: Organization and meta-thinking (thinking about thinking): See the big picture
The method takes into account how the brain works and works from the assumption that the brain is affected by chemical substances. These are different when we for example are careful from when we are positive.
Since we can not think all these different types of thoughts at the same time, it is smart to separate them.
De Bono believes that most people out of habit use only a few of these ways of thinking. You can check if this is the case for you yourself.
If you remember this learning strategy, and use it when dealing with a task, you will be more effective in your work. If you choose to use the tool in group work and give group members a specific category, their contributions will be easily categories and you would avoid for example that the black hat is in constant conflict with the green hat.
You can use the method in different situations, for example:
- For individual work
You put on all the hats (proverbially, and one after the other) and evaluate the subject matter with these hats as a starting point - For group work
Everyone in the group can wear the same hat at the same time – e.g. everyone first wears the blue hat to agree on how a project meeting should be conducted, and then take on the others in turn - In your assessment of what others say
You can classify what is said in a lecture or discussion, or you can try on the hats when going through a text.
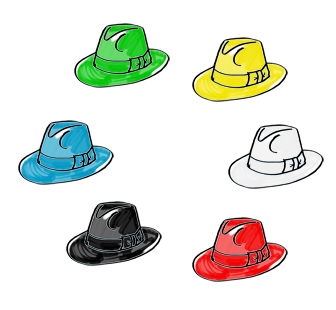
Explanation of the hats
It is a good idea to get an overview of the goals and scope of the job before you start, which means it is best to start with the blue hat.
 |
Blue hat Blue thinking is focused on processes and procedures. Here it is important to keep an overview of structures, methods and protocols. Take a step back and look carefully at how the situation is handled. What do we want to achieve? Where do we start? How much time do we have? What do we do next? Represents control and organization. Overview. |
 |
White hat With this hat you go for hard facts: The information without emotions. You want more information on the subject. What do I know? What information am I missing? How can I get the information I need? |
 |
Red hat Both positive and negative emotions. How do I feel about this? What are my reactions? Does it feel right? Intuition and emotions that should not be justified or explained. Subjectively. |
 |
Black hat When you put on the black hat, you look for the negative consequences. What are the weaknesses? What problems can occur? What is wrong? Reservations and caution, focus on dangerous sides. Objectively. |
 |
Yellow hat This is the opposite of black. Here you look at the positive consequences, the best possible outcome. What are the benefits? Why is it worth trying? How can this contribute to simplification or improvement? Allows visions and dreams. Objectively and speculatively. |
 |
Green hat With green, you think of innovation and new ideas. Think outside the box and look for less obvious alternatives. What is possible? What ideas do we have? What can we change? How can we develop this further? Used for idea creation and solution proposals, to look for alternatives. Speculative. |